 |
Mountain Building |
 |

 |
Mountain Building |
 |

Folding is frequently seen during mountain building. There are many types of folds from microscopic to macroscopic but almost all are a result of compressional forces.
Anticlines are formed by arching or upfolding of rock layers. In an anticline, the oldest rock layers are found in the center of the fold.

Anticline
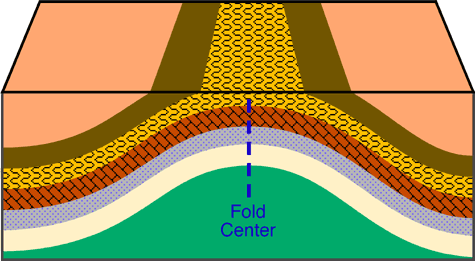
Anticline Diagram
A syncline is created by the downfolding of rock layers until a trough is formed. In a syncline, the youngest rock layers are found in the center.

Syncline

Syncline Diagram

Syncline
Anticlines and synclines can be symmetrical, asymmetrical or asymmetrical overturned. An asymmetrical overturned fold occurs when one limb is tilted beyond vertical. It is also important to note that anticlines and synclines plunge on their edges.
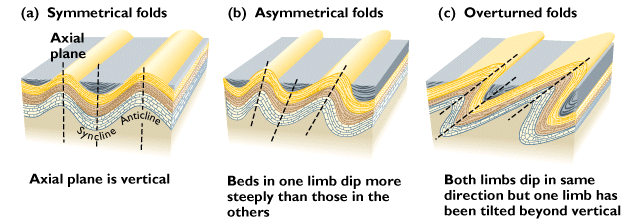
Diagram of anticline and syncline: symmetrical, asymmetrical, & asymmetrical overturned.

Diagram of plunges.

Diagram of a monocline.

Picture of a monocline.
Monoclines are large step like folds found in horizontal sedimentary strata.

Picture of a dome: Black Hills (hint)
Domes are circular or elongated structures generated when basement rock upwarps to deform overlying sedimentary strata.
Basins are also circular or elongated structures, but they are generated by the downwarping of basement rock. In basins, the oldest rock is found along the edges of the basin while the younger rock is found in the center of the basin.
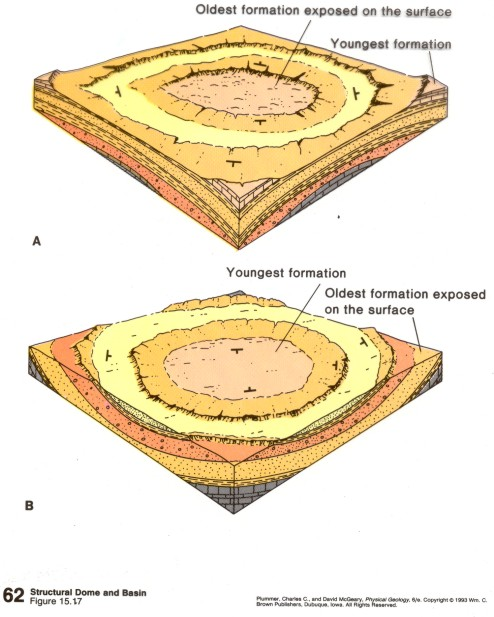
Diagram of a basin.

Diagram of a basin.
Back to Mountain Building Page 1 |
Mountain Building Page 3 |
Go To Mountain Building Assignments |