 |
EARTHQUAKES |
 |

Earthquakes
 The study of earthquakes is seismology.
The study of earthquakes is seismology.
- seismographs - instruments that read earthquake waves
- A weight is suspended from a support attached to bedrock
- The inertia of the weight keeps it stationary while the Earth and support vibrate
- The movement is recorded on a rotating drum creating a seismogram
Waves
- Surface waves - waves that travel along the outer layer of the Earth
- Slowest of the waves
- Up and down, side to side in a horizontal plane
- Cause the greatest amount of damage
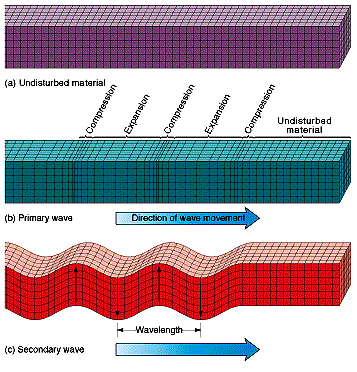
- Body waves - waves that travel through the Earth's interior
- P waves (primary)
- push-pull waves
- Compress and expand rocks in the direction the wave is traveling
- Travels through all materials
- Fastest type of wave
- S waves (secondary)
- Shake the Earth at right angles to their direction of travel
- Will not transmit through fluids
- Epicenter - the location on the surface directly above the focus
- The speed of the waves can be used to determine the epicenter
- The farther the station, the greater the time between wave arrivals






 The study of earthquakes is seismology.
The study of earthquakes is seismology.
